Real-time monitoring of InfiniBand networks, GPU temperatures, and Slurm job status to enhance cluster operational efficiency
This case study demonstrates how to build a comprehensive HPC cluster monitoring system using Grafana, enabling real-time monitoring and performance analysis of critical resources. By integrating Prometheus, Telegraf, and custom data collectors, we established a complete monitoring solution for a research institution's HPC cluster, covering multiple dimensions including networking, computing, and job scheduling.
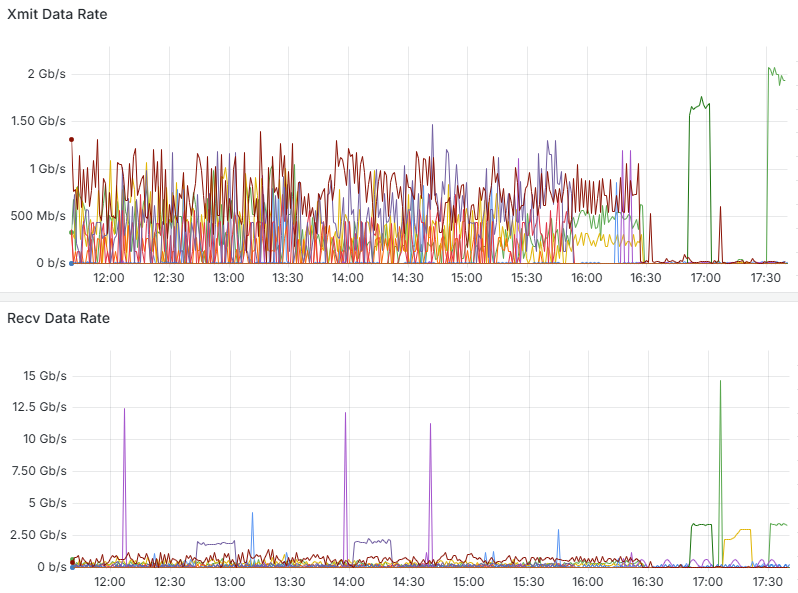
The above graph shows the send (Xmit) and receive (Recv) data rates of the HPC cluster's InfiniBand network. From the monitoring data, we can observe:
Through InfiniBand network traffic monitoring, administrators can:
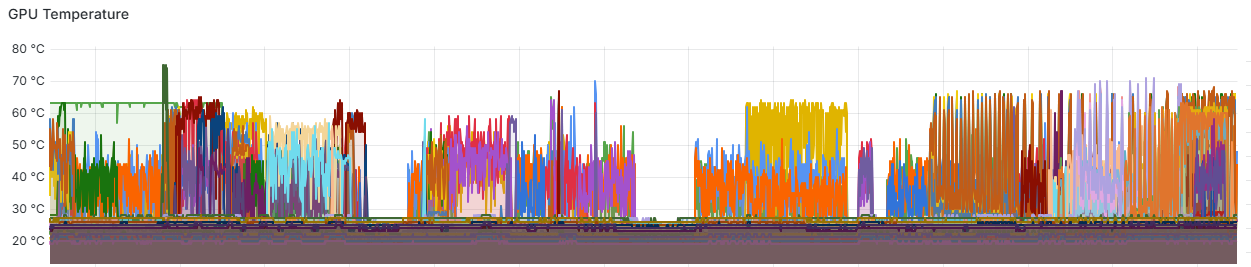
The above graph shows the temperature trends of GPU devices in the cluster. From the monitoring data, we can observe:
Through GPU temperature monitoring, administrators can:
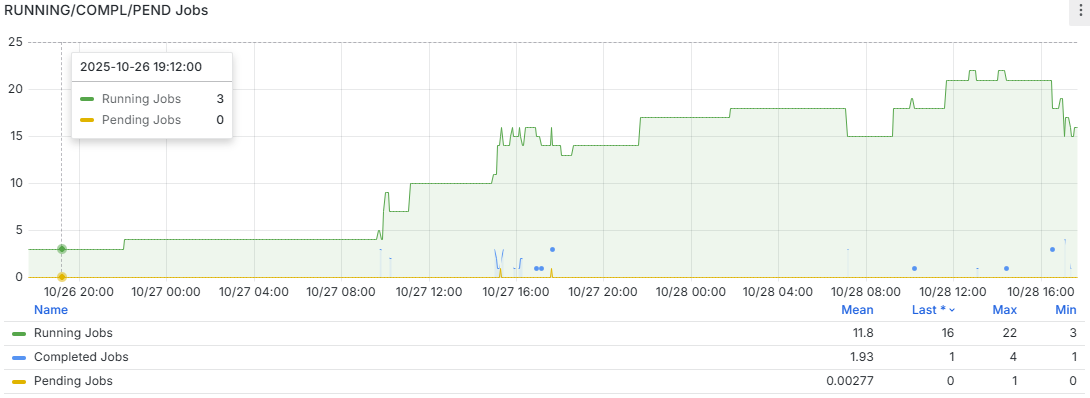
The above graph shows job running status statistics based on the Slurm scheduling system. From the monitoring data, we can observe:
Through Slurm job status monitoring, administrators can:
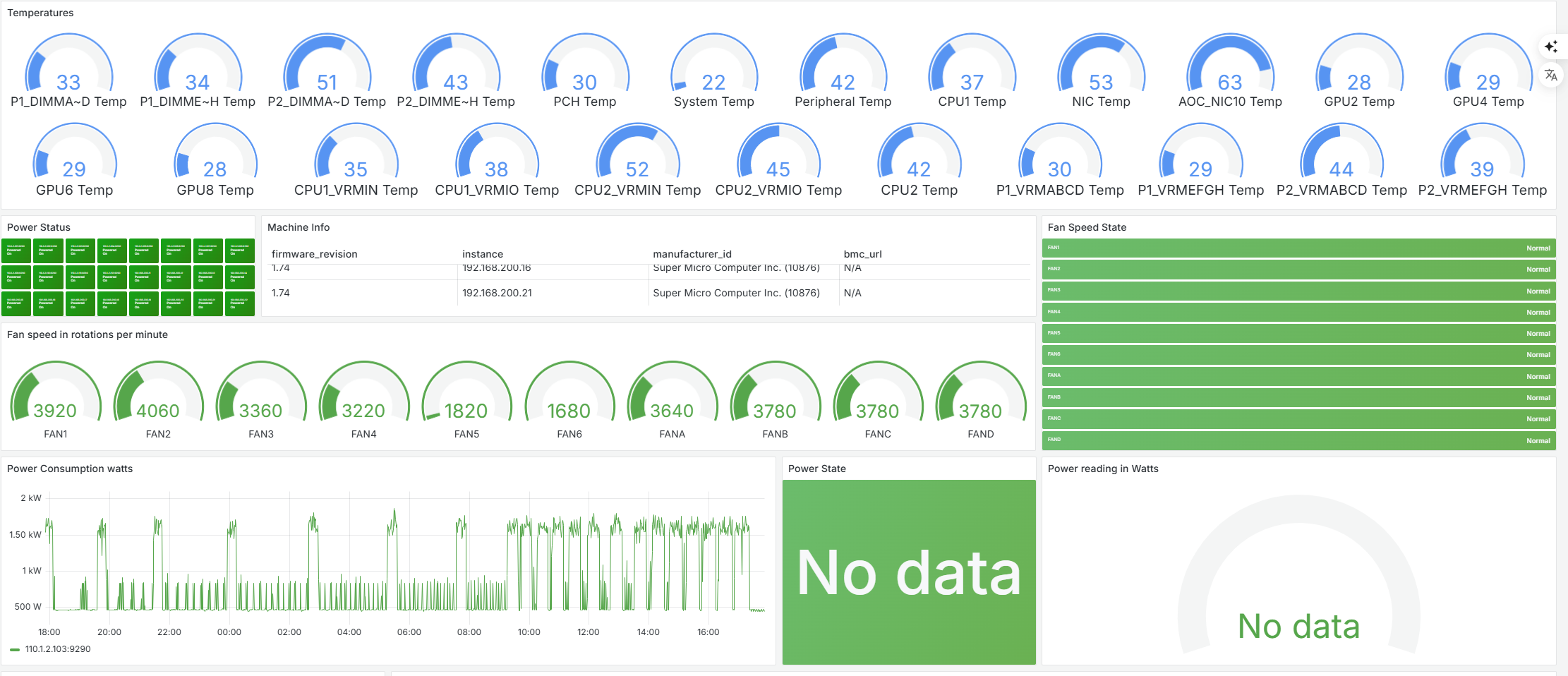
The above dashboard displays comprehensive IPMI sensor data from the HPC cluster nodes, including temperature readings from various components and power consumption metrics. From the monitoring data, we can observe:
Through IPMI sensor and power monitoring, administrators can:
Our monitoring solution delivered measurable improvements across multiple performance metrics
By identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks, overall cluster computing efficiency increased by 23%, and average job completion time was reduced by 18%.
Average system fault detection time was reduced from hours to minutes, preventive maintenance reduced unplanned downtime, and annual maintenance costs decreased by approximately 35%.
Average cluster resource utilization increased from 65% to 78%, peak period resource allocation became more reasonable, and user satisfaction significantly improved.
The Grafana monitoring system has provided us with unprecedented cluster visualization capabilities. Now we can track system status in real-time, respond quickly to anomalies, and make more informed expansion decisions based on historical data. This has greatly improved our research efficiency and resource utilization.
We can customize a comprehensive monitoring system for your HPC environment to improve operational efficiency and resource utilization.